Creating Tokens
"Token
s" are digital assets that can be traded, sold, or used on the Enjin Blockchain.- Some Enjin Coin on Enjin Matrixchain to process transactions and at least 0.01 ENJ for the Token Account Deposit. You can obtain cENJ (Canary ENJ) for testing from the Canary faucet.
- An Enjin Platform Account.
- A Collection to place the tokens in.
Enjin Blockchain allows you to create customized Token ID
structures. This flexibility enables you to organize your tokens in various ways that suit your needs.- For Multi-Unit Tokens These tokens are identical in value and function, and therefore, they all share the same Token ID. This commonality in ID reflects their interchangeable nature. For instance, all units of a specific cryptocurrency like Bitcoin would have the same identification as they hold the same value and are indistinguishable from one another in terms of usage and worth.
- For Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Every NFT has a unique Token ID that sets it apart from other tokens, even within the same collection. This unique ID is crucial for establishing the individuality and provenance of each NFT, which could represent anything from digital art to ownership rights over a virtual asset.
Before minting the Mainnet versions of your Tokens, that will be used in your live economy. Make sure to take a look at the best practices for Token ID structure.
There are two ways to use the Create Asset functionalities:
Option A. Using the Enjin Dashboard
In the Platform menu, navigate to "Tokens". Then, click the "Create Token" button.
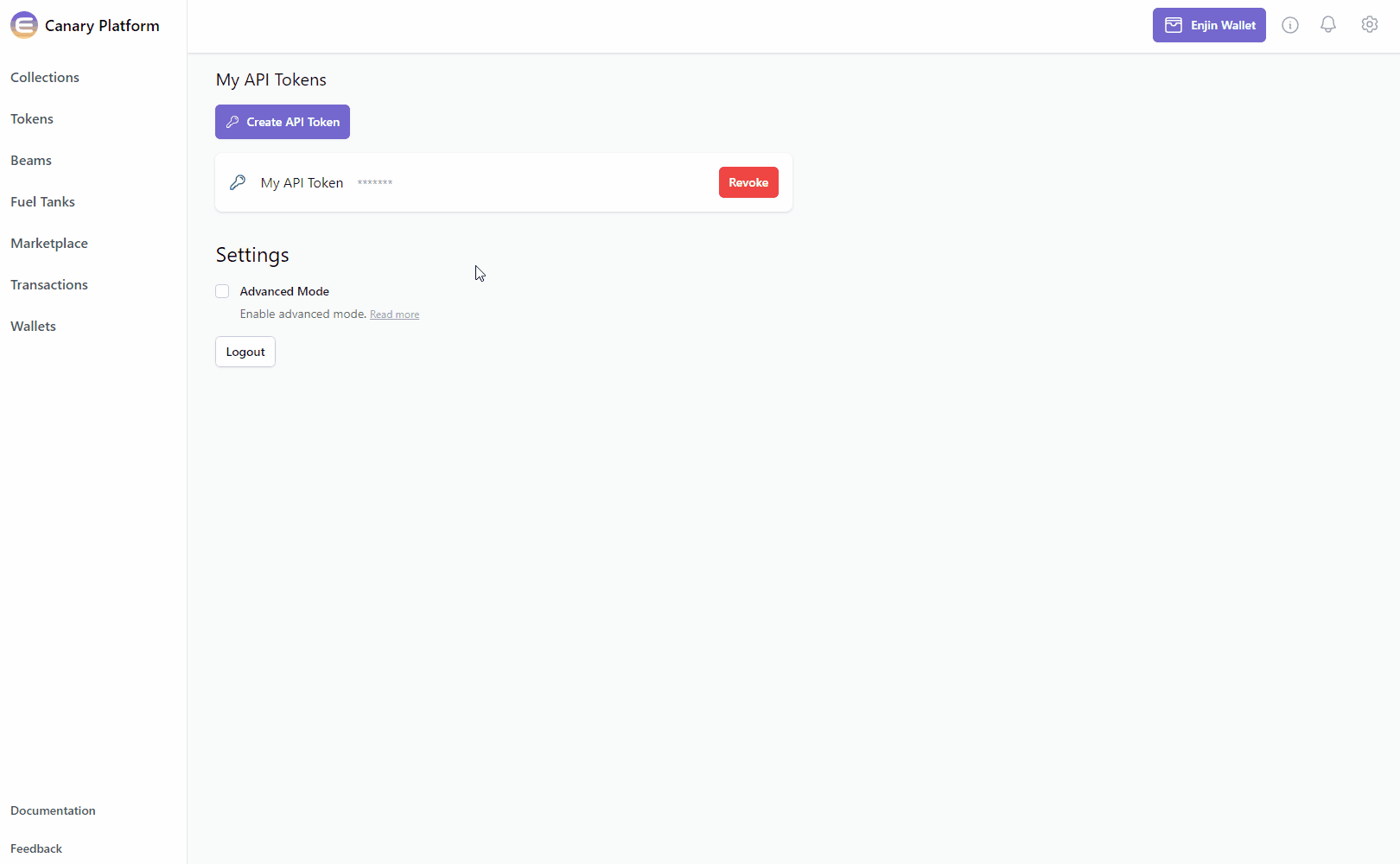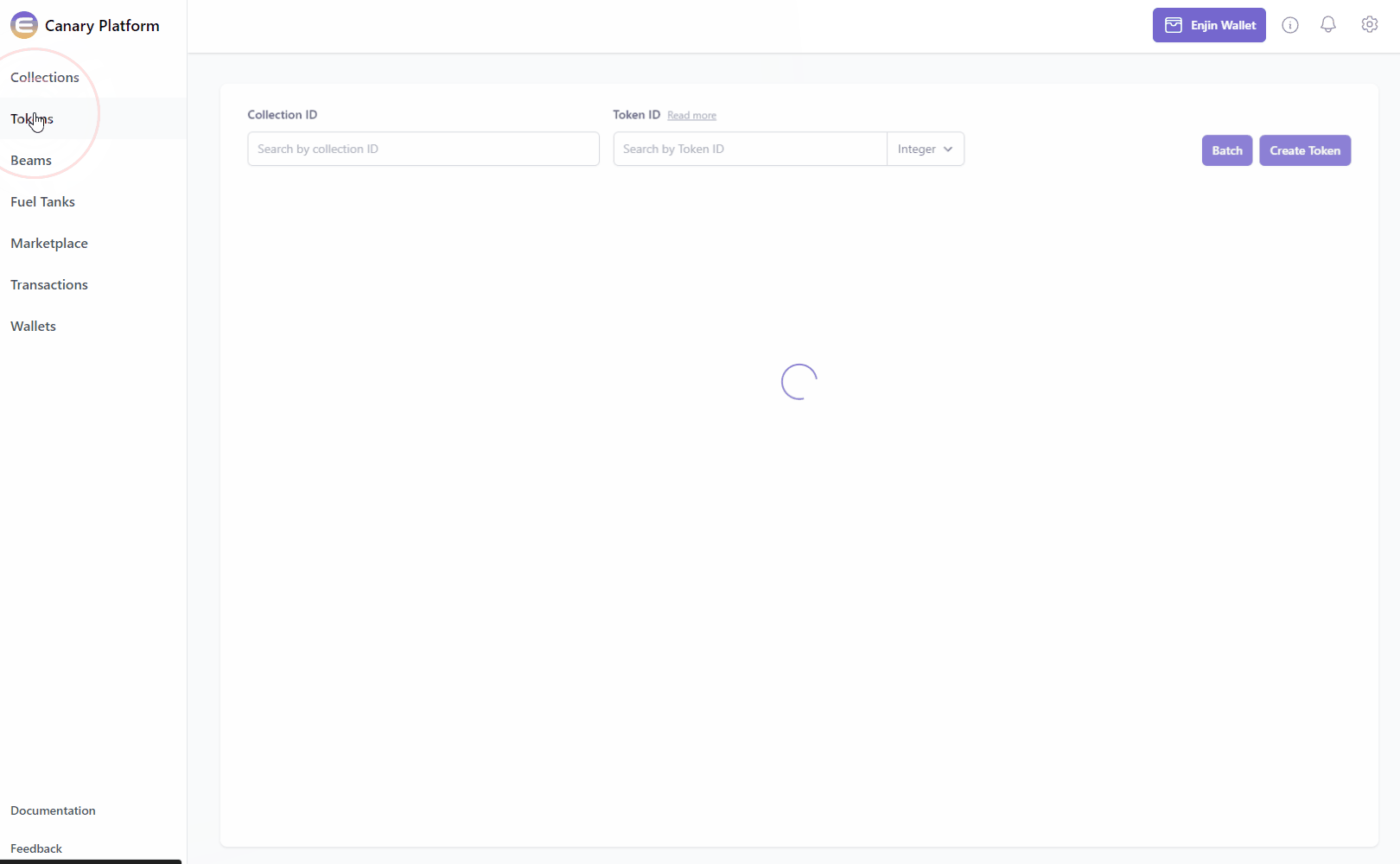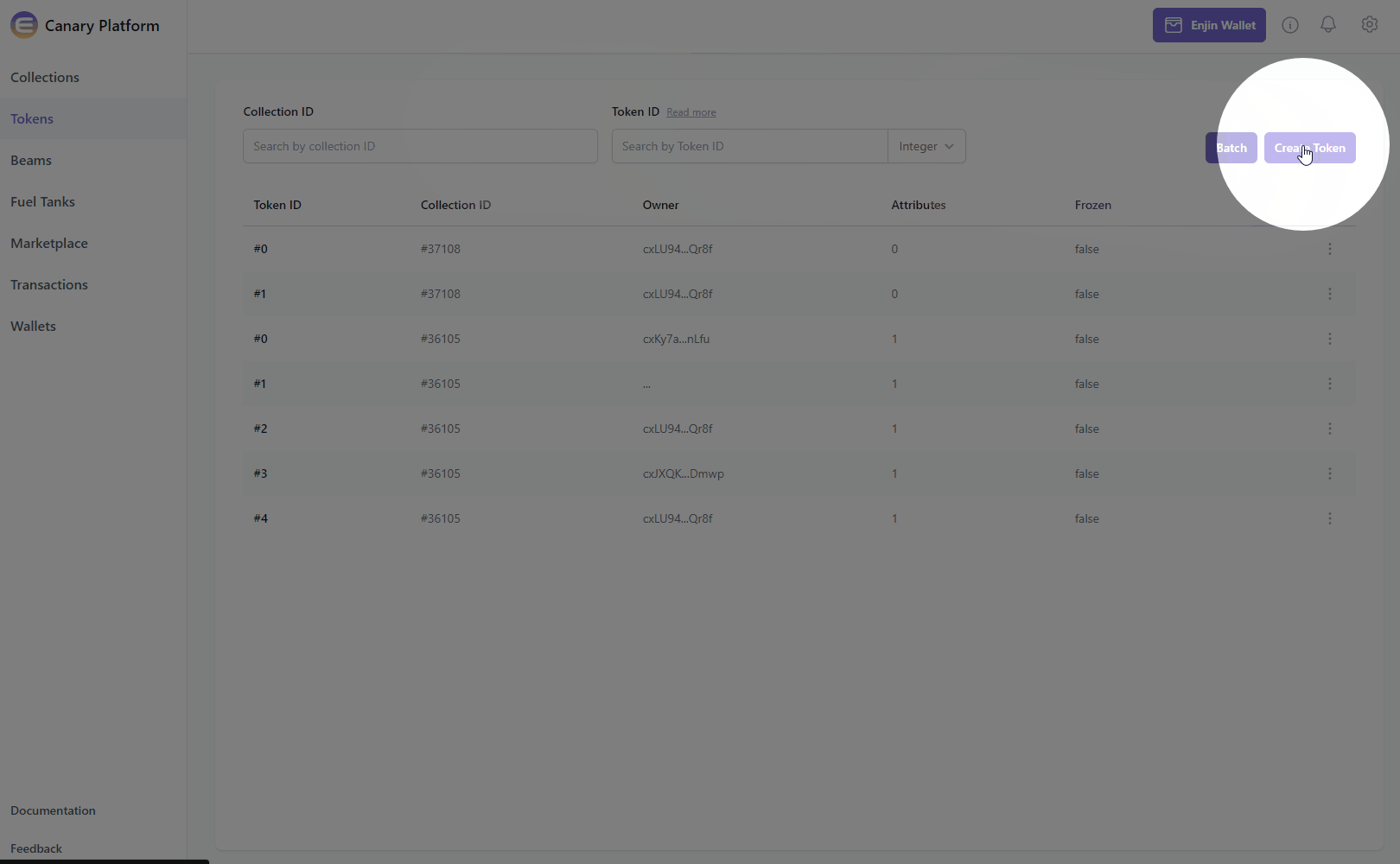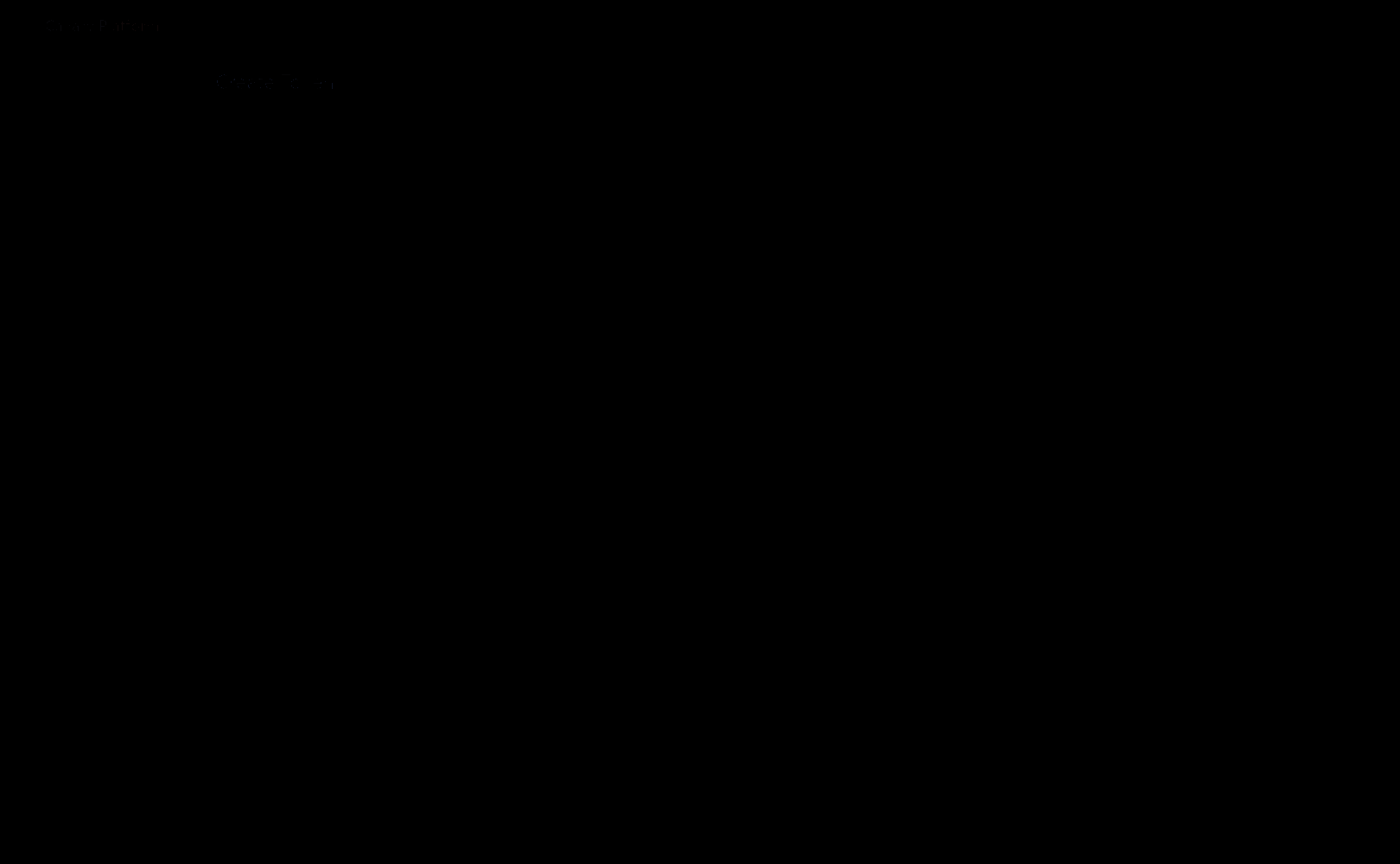
From here, you can customize your collection's Mint Policy, Market Policy, and Attributes.
- Create Token Section - Basic token options. Make sure to select the Collection ID you wish to mint the token in, the token ID, and the recipient in the corresponding fields. Make sure to check out the TokenID Structure Best Practices.
- Cap - The token cap (if required).
- The Infinite supply type is the most flexible. With this model, there is no limit to how many tokens can be minted or be in circulation. The collection owner can always mint additional units, making it ideal for use cases that require an ever-expanding token supply.
- The Fixed supply type offers a balanced approach between flexibility and control. This model allows the collection owner to mint new tokens as long as the circulating supply does not exceed the predetermined max supply. Burned tokens can be re-minted, ensuring the total supply remains constant.
- The Collapsing supply type is the most strict. This supply type allows the collection owner to mint new tokens as long as the circulating supply does not exceed the max supply. However, burning tokens reduces the max supply, meaning burned tokens cannot be re-minted. This ensures a non-increasing supply, suitable for use cases that require strict control over the token's total amount in circulation.
- Token Royalty Settings - Configures royalties for each marketplace sale of this token.
- Attributes - Add details to your token using key-value pairs. Standard keys like
nameanddescriptionallow applications to display your content correctly. You can also use theURIto link to a JSON file hosting your metadata. For more information, see the Metadata Standard page.
For a comprehensive view and detail of all available arguments please refer to our API Reference.
Once you're satisfied with the options, click on the "Create" button at the bottom right corner to create the request.
The Transaction Request will then appear in the "Transactions" menu.
Since this request requires a Transaction
, it'll need to be signed with your Wallet.- If a Wallet Daemon is running and configured, the transaction request will be signed automatically.
- If a wallet is connected such as the Enjin Wallet or Polkadot.js, the transaction must be signed manually by clicking the "Sign" button and approving the signature request in your wallet.
Once your token is created, lets give it a new look by Adding Metadata
Option B. Using the Enjin API & SDKs
CreateToken mutation enables you to create a new token within an existing collection. This operation is essential for introducing new digital assets, and it allows you to define various attributes and characteristics for the newly created token.
- GraphQL
- cURL
- c# SDK
- C++ SDK
- Javascript
- Node.js
- Python
mutation CreateToken{
CreateToken(
recipient: "cxLU94nRz1en6gHnXnYPyTdtcZZ9dqBasexvexjArj4V1Qr8f" #The recipient of the initial supply
collectionId: 2406 #Set the collection ID
params:{
tokenId: {integer: 0} #Set the token ID
initialSupply: 1 #Mint initial supply
cap: {type: INFINITE}} #Define supply type
) {
id
method
state
}
}
curl --location 'https://platform.canary.enjin.io/graphql' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'Authorization: enjin_api_key' \
-d '{"query":"mutation CreateToken(\r\n $recipient: String!\r\n $collection_id: BigInt!\r\n $token_id: BigInt\r\n $initial_supply: BigInt\r\n $cap: TokenMintCapType!\r\n) {\r\n CreateToken(\r\n recipient: $recipient\r\n collectionId: $collection_id\r\n params: {\r\n tokenId: { integer: $token_id }\r\n initialSupply: $initial_supply\r\n cap: { type: $cap }\r\n }\r\n ) {\r\n id\r\n method\r\n state\r\n }\r\n}","variables":{"recipient":"cxLU94nRz1en6gHnXnYPyTdtcZZ9dqBasexvexjArj4V1Qr8f","collection_id":91829,"token_id":0,"initial_supply":1,"cap":"INFINITE"}}'
using System.Text.Json;
using Enjin.Platform.Sdk;
// Define the token parameters
var tokenParams = new CreateTokenParams()
.SetTokenId(new EncodableTokenIdInput().SetInteger(0)) //Set the token ID
.SetInitialSupply(1) //Mint initial supply
.SetCap(new TokenMintCap().SetType(TokenMintCapType.Infinite)); //Define supply type
// Setup the mutation
var createToken = new CreateToken()
.SetRecipient("cxLU94nRz1en6gHnXnYPyTdtcZZ9dqBasexvexjArj4V1Qr8f") //The recipient of the initial supply
.SetCollectionId(2406) //Set the collection ID
.SetParams(tokenParams); //Set the previously defined token params
// Define and assign the return data fragment to the mutation
var createTokenFragment = new TransactionFragment()
.WithId()
.WithMethod()
.WithState();
createToken.Fragment(createTokenFragment);
// Create and auth a client to send the request to the platform
var client = PlatformClient.Builder()
.SetBaseAddress("https://platform.canary.enjin.io")
.Build();
client.Auth("Your_Platform_Token_Here");
// Send the request and write the output to the console.
// Only the fields that were requested in the fragment will be filled in,
// other fields which weren't requested in the fragment will be set to null.
var response = await client.SendCreateToken(createToken);
Console.WriteLine(JsonSerializer.Serialize(response.Result.Data));
#include "EnjinPlatformSdk/CoreMutations.hpp"
#include <iostream>
using namespace enjin::platform::sdk;
using namespace std;
int main() {
// Setup mutation data
shared_ptr<CreateTokenParams> tokenParams = make_shared<CreateTokenParams>();
shared_ptr tokenId = make_shared<EncodableTokenIdInput>();
tokenId->SetInteger(make_shared<SerializableString>("0"));
shared_ptr<TokenMintCap> tokenMintCap = make_shared<TokenMintCap>();
tokenMintCap->SetType(TokenMintCapType::Infinite);
tokenParams->SetTokenId(tokenId);
tokenParams->SetInitialSupply(make_shared<SerializableString>("1"));
tokenParams->SetCap(tokenMintCap);
// Setup mutation
CreateToken createToken = CreateToken();
createToken
.SetRecipient(make_shared<SerializableString>("cxLU94nRz1en6gHnXnYPyTdtcZZ9dqBasexvexjArj4V1Qr8f"))
.SetCollectionId(make_shared<SerializableString>("2406"))
.SetParams(tokenParams);
// Define and assign the return data fragment to the mutation
shared_ptr<TransactionFragment> transactionFragment = make_shared<TransactionFragment>();
transactionFragment
->WithId()
.WithMethod()
.WithState();
createToken.SetFragment(transactionFragment);
// Create and auth a client to send the request to the platform
unique_ptr<PlatformClient> client = PlatformClient::Builder()
.SetBaseAddress("https://platform.canary.enjin.io")
.Build();
client->Auth("Your_Platform_Token_Here");
// Send the request then get the response and write the output to the console.
// Only the fields that were requested in the fragment will be filled in,
// other fields which weren't requested in the fragment will be set to null.
future<shared_ptr<IPlatformResponse<GraphQlResponse<Transaction>>>> futureResponse = SendCreateToken(*client, createToken);
// Get the platform response holding the HTTP data
PlatformResponsePtr<GraphQlResponse<Transaction>> response = futureResponse.get();
// Get the result, a GraphQL response, holding the GraphQL data
const optional<GraphQlResponse<Transaction>>& gqlResult = response->GetResult();
// Write the result data to the console
if (gqlResult.has_value() && gqlResult->IsSuccess())
{
const optional<Transaction>& transaction = gqlResult->GetData()->GetResult();
std::cout << to_string(transaction->GetId().value()) << std::endl;
std::cout << ToString(transaction->GetMethod().value()) << std::endl;
}
// Write any error messages to the console
if (gqlResult.has_value() && gqlResult->HasErrors())
{
const optional<vector<GraphQlError>>& errors = gqlResult->GetErrors();
for (const GraphQlError& error : errors.value()) {
std::cout << error.GetMessage().value() << std::endl;
}
}
client.reset();
return 0;
}
fetch('https://platform.canary.enjin.io/graphql', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {'Content-Type': 'application/json','Authorization': 'Your_Platform_Token_Here'},
body: JSON.stringify({
query: `
mutation CreateToken(
$recipient: String!
$collection_id: BigInt!
$token_id: BigInt
$initial_supply: BigInt
$cap: TokenMintCapType!
) {
CreateToken(
recipient: $recipient
collectionId: $collection_id
params: {
tokenId: { integer: $token_id }
initialSupply: $initial_supply
cap: { type: $cap }
}
) {
id
method
state
}
}
`,
variables: {
recipient: "cxLU94nRz1en6gHnXnYPyTdtcZZ9dqBasexvexjArj4V1Qr8f", //The recipient of the initial supply
collection_id: 2406, //Specify the collection ID
token_id: 0, //Specify the token ID
initial_supply: 1, //Mint initial supply
cap: "INFINITE" //Define supply type
}
}),
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => console.log(data));
const axios = require('axios');
axios.post('https://platform.canary.enjin.io/graphql', {
query: `
mutation CreateToken(
$recipient: String!
$collection_id: BigInt!
$token_id: BigInt
$initial_supply: BigInt
$cap: TokenMintCapType!
) {
CreateToken(
recipient: $recipient
collectionId: $collection_id
params: {
tokenId: { integer: $token_id }
initialSupply: $initial_supply
cap: { type: $cap }
}
) {
id
method
state
}
}
`,
variables: {
recipient: "cxLU94nRz1en6gHnXnYPyTdtcZZ9dqBasexvexjArj4V1Qr8f", //The recipient of the initial supply
collection_id: 2406, //Specify the collection ID
token_id: 0, //Specify the token ID
initial_supply: 1, //Mint initial supply
cap: "INFINITE" //Define supply type
}
}, {
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json', 'Authorization': 'Your_Platform_Token_Here' }
})
.then(response => console.log(response.data))
.catch(error => console.error(error));
import requests
query = '''
mutation CreateToken(
$recipient: String!
$collection_id: BigInt!
$token_id: BigInt
$initial_supply: BigInt
$cap: TokenMintCapType!
) {
CreateToken(
recipient: $recipient
collectionId: $collection_id
params: {
tokenId: { integer: $token_id }
initialSupply: $initial_supply
cap: { type: $cap }
}
) {
id
method
state
}
}
'''
variables = {
'recipient': 'cxLU94nRz1en6gHnXnYPyTdtcZZ9dqBasexvexjArj4V1Qr8f', #The recipient of the initial supply
'collection_id': 2406, #Specify the collection ID
'token_id': 0, #Specify the token ID
'initial_supply': 1, #Mint initial supply
'cap': 'INFINITE' #Define supply type
}
response = requests.post('https://platform.canary.enjin.io/graphql',
json={'query': query, 'variables': variables},
headers={'Content-Type': 'application/json', 'Authorization': 'Your_Platform_Token_Here'}
)
print(response.json())
A WebSocket event will also be fired so you can pick up the changes in real-time by listening to the app channel on the WebSocket.
For Token ID management, head to Best Practices > TokenID Structure
For a comprehensive view of all available arguments for queries and mutations, please refer to our API Reference. This resource will guide you on how to use the GraphiQL Playground to explore the full structure and functionality of our API.
For instance, you'll find settings such as adding attributes/royalties/supply type and much more with the CreateTokenParams argument, or the ability to sign using a managed wallet with the signingAccount argument.
To add metadata to your token, go to the Adding Metadata tutorial.